Post 4 Traveling Through a Network
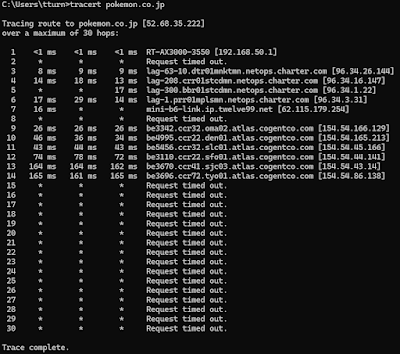
I used the Ping command on my computer for multiple websites, and this is what happened. I used Google.com, pokemon.co.jp, and korea.net. The Ping results that I got from all three different websites varied and were all different. Google.com was sent four packets, and received the four packets with a minimum round trip of 40ms, a maximum of 46ms, and an average of 42ms. Pokemon.co.jp was sent four packets; however, they received zero of the four packets, with a loss of 100%. Korea.net was sent four packets, received the four packets with a minimum of 207ms, maximum 211ms, for an average of 208ms round-trip time in milliseconds.
I used the Traceroute command on my computer for multiple websites, and this is what happened. Tracerouting the same three websites that I pinged earlier helped give me a better explanation as to why some pings are higher and why some requests timed out. The ping command can help troubleshoot some internet connection problems because it checks and pings a host address to see if it is reachable. The traceroute command allows me to check and follow which route the packets are taking to reach their destination, because of this, it allows me to see where packets are being lost, which can also help troubleshoot certain internet connection problems. Round-trip time and geographical location go hand in hand because distance matters; the farther the geographical location is, the longer the round-trip time is due to the extra distance that has to be covered. One reason why a ping or traceroute command can time out or give an error is if the host/device that you are trying to ping is off/not responding. A second reason why a ping or traceroute command can time out or give an error is if a network has security restrictions, such as a firewall that blocks the packets.



Comments
Post a Comment